Evaluation of the Degree of Dissociation of a Congruent
Compound Fe2Ti across the Bjerrum–Guggenheim Coefficient
Vera Vladimirovna Tolokonnikova
Sailaubai Baisanov
Gauhar Sarsengaliqyzy Yerekeyeva
Gulnar Itimirovna Narikbayeva
Irina Yaroslavovna Korsukova
Correspondence: tolokon‐splav@mail.ru
Abstract: This article describes a new quantitative evaluation method for the degree of dissociation
of a compound depending on the curvature of the liquidus line curve. The main point of this
method was to determine the specific expressions for dissociation parameters according to the
mathematical model of the crystallization line of the compound on the phase diagram. This was
based on generally accepted thermodynamic relations. Empirically, it has now been established
that for many types of phase equilibria, a common feature is the presence of a correlation dependence
between the ratios of the real Gibbs energy of the distribution of components to its ideal
component. The osmotic coefficient of Bjerrum–Guggenheim was used as a measure of the deviation
of the system from ideality. This coefficient can be in an analytical form depending on the
temperature and composition of the phases. The obtained correlation dependence of the osmotic
coefficient of Bjerrum–Guggenheim on the ratio of the activity of the liquid and solid phase has
been used to develop a mathematical apparatus to analytically describe the lines and surfaces of
the crystallization phases. Accordingly, a single analytical basis, as a universal dependence of the
modified Schröder–Le Chatelier equation, has been applied. Based on this equation, the conditions
have been defined to develop an equilibrium method with which to calculate the thermal dissociation
of chemical compounds. The principle of this method has been examined based on the
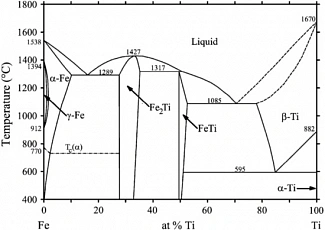
two‐component iron‐titanium system. The numerical results of the degree of dissociation of the
congruent Fe2Ti compound have been obtained using the Gibbs energy of the dissociation reaction
and the reaction constant. However, it has been found that the degree of dissociation in the compound
Fe2Ti was 0.04%. Demonstrative material for the behavior of the osmotic coefficient of
Bjerrum–Guggenheim under boundary conditions has been presented as an assessment criterion of
melt structures. The diagrams of the Фi function of the crystallizing phases near the melting temperature
of congruently melting compounds (Tm.) have been mathematically studied.
Keywords: phase diagrams; congruent compound; the monovariant phase equilibrium lines; the
degree of dissociation; Gibbs energy; Bjerrum–Guggenheim coefficient
https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122132
Evaluation of the Degree of Dissociation of a Congruent Compound Fe2Ti across the Bjerrum–Guggenheim Coefficient
Заказать услугу
Оформите заявку на сайте, мы свяжемся с вами в ближайшее время и ответим на все интересующие вопросы.
Документы
metals-12-02132
Размер:
621.2 Кб